The sales day book is one of the main books of prime entry when it comes to accounting. In this guide, you’ll learn more about what’s recorded in this document, as well as how it fits in when it comes to double-entry bookkeeping and sales journals.
What is a Sales Day Book?
The sales day book is a list of credit sales made by a business. It is filled out using copies of sales invoices raised, which are source records, summarising essential information about sales made including:
- Invoice date
- Customer name
- Amount
- Sales tax or VAT
- Value of products or services sold
The exact information recorded will vary business to business, depending on their needs. It should be noted that the sales day book is only used to record the day-to-day sales of a business – credit notes will be record separately in the sales return day book and other sales such as cash sales or non-trading income like the sale of land will be recorded elsewhere.
Example Sales Day Book
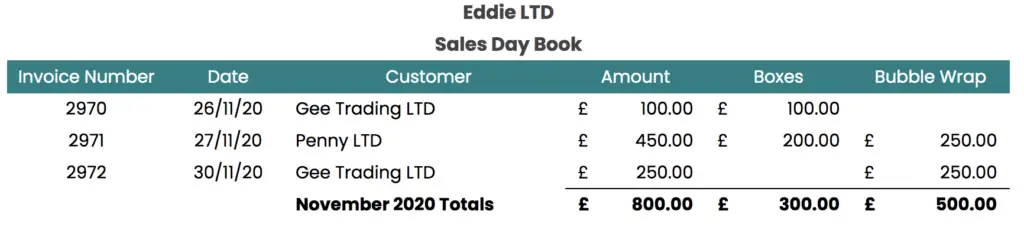
Here is a sample sales day book for Eddie LTD, where sales are analysed by product type:
What is a Sales Day Book Used For?
The sales day book helps businesses keep track of their sales so they can see how much they are selling and across which products. It also forms the basis for recording sales in the general ledger, from which the trial balance is prepared and finally the financial accounts.
In summary, the following entries will be made using the information contained in the sales day book:
- Updates to the individual sales ledgers to record how much individual customers owe;
- Weekly or monthly sales journal to record sales in the general ledger;
Sales Day Book v. Sales Ledgers
The sales day book is normally updated on a daily basis so all invoices captured are noted in a list. Then either daily or weekly, whichever is appropriate to the business, individual customer sales ledgers are updated.
Individual sales ledgers are a record kept for each customer logging invoices raised and payments made. That way it is clear how much money each customer owes (trade debtors).
In the example above, two sales accounts will need to be updated – GEE Trading LTD and Penny LTD.

Sales Journal
Periodically, normally weekly or monthly, the sales day book is closed off and the totals are transferred to the general ledger using a journal entry. The sales journal records the monthly sales of the business in the profit & loss account by debiting the sales ledger control account and crediting sales (also referred to as turnover or income).
In the example above, at the end of November 2020 the sales journal would be:
- Dr Sales ledger control account £800.00
- Cr Turnover – Boxes £300.00
- Cr Turnover – Bubblewrap £500.00
Being November 2020 sales
If Eddie LTD was VAT registered the sales journal will contain an entry for sales tax payable.