The books of prime entry are the first steps of summarising financial information. Businesses generate source records almost every time they make a transaction. The details contained in these records somehow need to be extracted and summarised in such a way that financial statements can be prepared which contain numbers giving an overview of how a business has performed. This is where the books of prime entry come into play.
Table of Contents
- 1. What are the Books of Prime Entry?
- 2. Why are the Books of Prime Entry Important?
- 3. How are the Books of Prime Entry Updated?
- 4. Control Accounts v. Books of Prime Entry
- 5. General Journal v. Books of Prime Entry
1. What are the Books of Prime Entry?
Once the source records have been collated, there needs to be a way to summarise the information contained in them so that essential information is noted down and ready for the next step in the accounting process.
In the old days, individual books were maintained as a summary of each of the key types of financial records and were also referred to as the books of original entry. Although computers take care of recording this information for us now, the concept is still the same, it’s just entered onto a screen instead.
There are six different types of books of prime entry:
- Sales Day Book
- Sales Returns Book
- Purchase Day Book
- Purchases Return Book
- Cash Book
- Petty Cash Book
1.1 Sales Day Book
The sales day book is a list of credit sales made by a business. It is filled out using copies of sales invoices raised (source records), summarising essential information about sales made including invoice date, customer name, sales price and sales tax.
1.2 Sales Returns Book
The sales return book is a list of credit notes raised by a business to cancel or reduce the value of sales invoices.
1.3 Purchase Day Book
The purchase day book is a list of credit purchases made by a business. It is filled out using copies of purchase invoices received, summarising essential information about purchases made including invoice date, supplier name, total price and sales tax added.
1.4 Purchases Return Book
The purchases return book is a list of credit notes received from suppliers in the event that purchase invoices needed to be cancelled or reduced in value for example due to errors or problems with products.
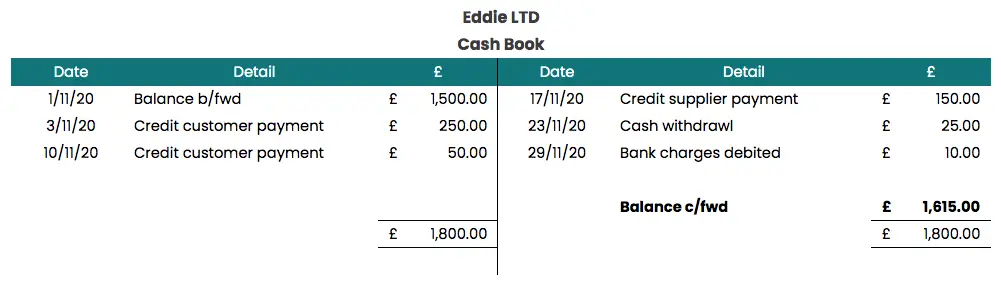
1.5 Cash Book
The cash book is a record of all the payments and receipts that come in and out of the business bank account, whether that is in the form of bank transfers, standing orders and direct debits.
1.6 Petty Cash Book
The petty cash book is a record of cash spent and received. Some businesses keep cash on their premises to pay for small day-to-day items such as milk or stationery. The petty cash book is a record of this spending and, if necessary, also customers who pay in cash.
2. Why are the Books of Prime Entry Important?
The main purpose of the prime entry books is to capture all the essential information needed to produce the financial accounts – which is the ultimate goal when it comes to accounting. It is important that this information is recorded accurately and in the way that is required for entry into the general ledger, using double-bookkeeping.
3. How is a Book of Prime Entry Updated?
Depending on the size of the business, each of the six books will need to be updated on a regular basis. For really large businesses a person or team may be assigned to one book in particular. For example the purchase day book may be updated by a purchase ledger team whose job it is to record every invoices that is issued to the business. For smaller businesses, they may be updated less regularly.
Nowadays, the books of prime entry are updated via an accounting software and copies of the prime records uploaded to be stored within the system. But years ago, the books would have been filled out by hand and hard copies of the source documents stored in folders.
4. Control Accounts v. Books of Prime Entry
The control account is part of the general ledger whereas the books of prime entry are simply a record of transactions. These transactions are then summarised for entry into the general ledger.
5. General Journal v. Books of Prime Entry
A general journal is an adjustment to the general ledger or post-trial balance stage whereas the books of prime entry are a record of transactions. If something is missed in the books of prime entry, then a general journal may be required to adjust for the missing transaction so that the financial statements are accurate.